The Role of BIM in Shaping the Next Generation of Saudi Arabia’s Smart Cities
The Role of BIM in Shaping the Next Generation of Saudi Arabia’s Smart Cities
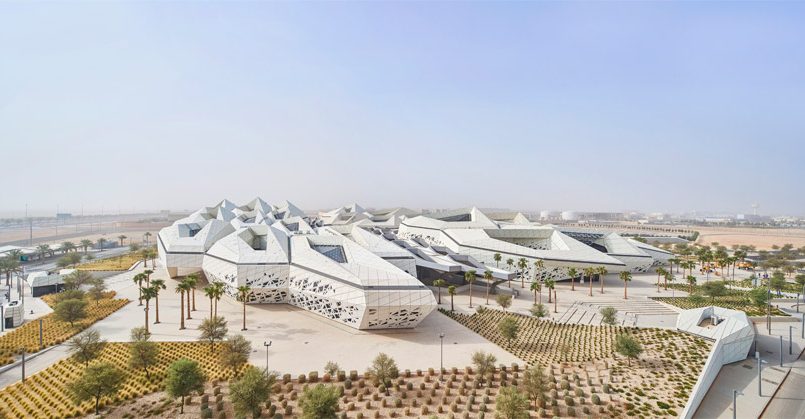
Globally, the architectural, engineering, and construction sectors have seen a transformation thanks to Building Information Modelling (BIM), which has been particularly important for the creation of contemporary smart cities. The ability to create digital representations of the functional and physical properties of space is made possible by this ground-breaking technology, which greatly improves the accuracy and efficiency of planning, designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure and buildings. BIM is at the vanguard of this transition, promoting innovation, sustainability, and smart urban management as Saudi Arabia moves closer to its Vision 2030 and into the era of smart cities.
Historical Roots and Evolution of BIM
BIM’s journey started in the 1970s with rudimentary modelling software and progressed through the years from simple 2D sketching tools to complex systems with the ability to visualise data in 3D, 4D (time), and 5D (cost). The rising complexity of building projects and the need for project management to be more efficient, economical, and environmentally conscious are reflected in this progression. The government of Saudi Arabia has increased the implementation of BIM technology as part of its drive to improve infrastructure development and incorporate international standards of sustainability and innovation into its real estate and urban development projects.

BIM and Public Engagement
Apart from its technical advantages, Building Information Modelling (BIM) is an effective instrument for stakeholder communication and public involvement. BIM helps the public and decision-makers comprehend the possible advantages and effects of urban development by producing realistic 3D visualisations of proposed projects. Transparency in this area promotes cooperation and confidence amongst the public, developers, and government organisations, which results in more sustainable and inclusive city planning procedures.
Neom: A Case Study in Advanced BIM Application
The ambitious mega-city project, NEOM, makes extensive use of BIM. The goal of this futuristic metropolis is to combine urban life, eco-friendly methods, and the newest technology. Project managers and engineers can now design with a comprehensive understanding of future growth, resource management, and environmental consequences thanks to the usage of BIM. Technology makes it possible to design buildings and infrastructure modularly, allowing them to change gradually as a city expands.
The Red Sea Project: Environmental and Architectural Precision
The Red Sea Development, a posh tourist destination driven by BIM technology, is another important project. It seeks to redefine sustainable development norms. BIM’s sophisticated modelling makes it easier to plan and execute with precision while protecting the fragile terrestrial and marine ecosystems. By using environmentally friendly materials and building techniques that reduce ecological disturbance, BIM, for example, aids in simulating environmental effects.
BIM in the Riyadh Metro Project
Another project where BIM is essential is the Riyadh Metro project, which is a component of the Riyadh Public Transport Project. This vast network, intended to lessen urban traffic jams and lower pollution levels, makes use of BIM to facilitate effective coordination between several foreign engineering firms and contractors. Before construction, station layouts and alignments may be seen thanks to the 3D models that were made, guaranteeing precision and compliance with safety standards.
Training and Innovation in BIM Implementation
Saudi Arabia is also making investments in BIM-focused innovation hubs and training programmes to facilitate the broad adoption of BIM. In order to prepare the future generation of engineers and architects, universities and technical institutions throughout the kingdom are starting to include BIM training into their curricula. Furthermore, government measures that encourage innovation in building technology complement these programmes, elevating BIM to a national priority.

Investment in BIM Infrastructure
As long as Saudi Arabia continues to support significant infrastructure projects, the government’s commitment to BIM infrastructure is essential. This includes not just buying BIM software and training classes, but also building digital twin platforms and BIM data warehouses. Saudi Arabia can promote creativity, effectiveness, and data-driven decision-making in the field of urban planning and development by centralising Building Information Modelling (BIM) data and promoting data sharing across partners in the public and commercial sectors.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Although there are obstacles to BIM adoption in Saudi Arabia, including data management and upfront high expenditures, the long-term advantages in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and environmental preservation are indisputable. The ability to handle large data and integrate IoT with BIM will improve operational efficiencies and support smart city efforts as more projects use BIM.

HYKAL Design
Conclusion
Building information modelling (BIM) is a key technology that Saudi Arabia is utilising to build smart cities. It improves the administration and building of urban infrastructure and adds substantially to the sustainability and efficiency of these settings. A new chapter in the history of urban development in the Kingdom is being written by the strategic application of BIM in large-scale projects like NEOM, the Red Sea Development, and the Riyadh Metro. These projects demonstrate the critical role that BIM will play in forming a future where smart technology, environmental sustainability, and creative urban planning converge.



