Digital Twin Technology: Shaping the Future of Urban Development in Saudi Arabia
Digital Twin Technology: Shaping the Future of Urban Development in Saudi Arabia
As Saudi Arabia advances in its ambitious Vision 2030 initiative, digital technologies are playing an increasingly vital role in reshaping the country’s urban landscape. Among the most transformative innovations is Digital Twin technology, which is revolutionizing the way cities, infrastructure, and buildings are designed, monitored, and managed. The Kingdom’s mega-projects, such as NEOM, the Red Sea Project, and Qiddiya, are embracing this technology to enhance urban development, efficiency, and sustainability.
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object, system, or process that simulates its real-world counterpart in real-time. This data-driven approach allows planners, architects, engineers, and policymakers to make informed decisions about urban growth, infrastructure management, and the future of cities. By harnessing data from sensors, IoT devices, and other technologies, digital twins provide actionable insights into everything from traffic patterns to energy consumption, leading to more efficient, sustainable, and resilient cities.
What is Digital Twin Technology?
Digital twins create dynamic, virtual models of physical spaces, infrastructure, or entire cities. These models are connected to real-time data sources, enabling stakeholders to track the performance of systems and structures, simulate different scenarios, and predict outcomes. This technology can simulate entire cities, districts, or individual assets such as buildings, bridges, or transportation networks.
The concept of a digital twin allows for predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and advanced scenario testing. It’s a highly useful tool for urban planning, helping cities plan better, avoid costly mistakes, and ensure smoother operations. In environments like Saudi Arabia, where rapid urbanization and development are underway, digital twins are essential for managing these expansive changes while ensuring sustainability and resilience.
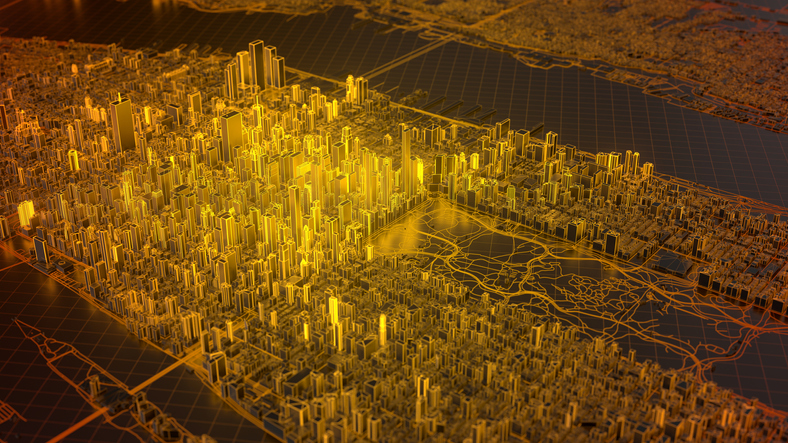

The Role of Digital Twins in Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, which aims to diversify the economy, reduce dependence on oil, and enhance quality of life, has ushered in a new era of technological advancement. This includes ambitious infrastructure projects like NEOM, a futuristic smart city, and the Red Sea Project, a luxury tourism development. Both of these projects—and many others across the Kingdom—are relying on Digital Twin technology to help visualize, plan, and manage their complexities.
For instance, NEOM is envisioned as a city of the future that will incorporate advanced technologies such as AI, robotics, and IoT. A digital twin of NEOM can help urban planners simulate the effects of various environmental, economic, and social scenarios, optimize urban systems like water distribution and energy management, and ensure the city operates sustainably from the outset. With real-time monitoring, the city’s infrastructure can be adjusted as needed, creating a more adaptable and responsive urban environment.
In cities like Riyadh, where rapid population growth and traffic congestion have become pressing issues, digital twins enable city planners to simulate traffic patterns, analyze air quality, and assess the efficiency of public transport systems. By creating a virtual model of Riyadh, planners can test the impact of new transportation projects (like the Riyadh Metro), green spaces, and even climate change, long before physical work begins.
Applications of Digital Twin Technology in Urban Development
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Management
Digital twins are an invaluable tool for managing Saudi Arabia’s rapidly growing cities. In a sprawling urban environment like Riyadh, where urban sprawl and population growth are major challenges, digital twins help city officials simulate traffic, energy use, water consumption, and more, optimizing urban planning efforts. This technology allows planners to test different urban designs, ensuring the most efficient and sustainable city layouts.
Additionally, digital twins can be used to simulate the performance of critical infrastructure like roads, bridges, and utilities, ensuring that these systems can handle future demands without costly delays. This ability to anticipate future problems and optimize designs before construction begins saves both time and money.
Building Design and Construction
Digital twins are changing the way buildings and infrastructure are designed. Architects and engineers can use digital twin models to test different design options, materials, and structural elements. This results in more accurate designs, faster construction timelines, and reduced risk during the building phase. For example, if a building is part of a larger urban development, its digital twin can be integrated into the broader city model, ensuring that it fits seamlessly into the existing infrastructure.
In Saudi Arabia, many new developments are designed with sustainability in mind. Digital twins help reduce resource consumption during the design and construction phases by enabling real-time energy modeling, optimizing the use of materials, and ensuring that structures are resilient to extreme temperatures and other environmental factors. This is especially important given Saudi Arabia’s efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and create environmentally sustainable cities.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Sustainability is a central tenet of Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, and digital twin technology is instrumental in achieving these goals. By providing real-time insights into energy use, waste, and resource management, digital twins help cities and businesses make informed decisions about reducing their environmental impact.
For example, digital twins can be used to model the energy consumption of buildings, transportation systems, and entire districts. These models can identify areas where energy efficiency can be improved, suggest changes to reduce carbon footprints, and even integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind. In a place like NEOM, which aims to be a global model for sustainability, digital twins will play a key role in optimizing energy use and integrating green technologies.
Maintenance and Facility Management
The ability to perform predictive maintenance is one of the most valuable applications of digital twin technology. By linking physical assets with real-time data, digital twins allow building and infrastructure managers to monitor the health of systems such as HVAC, electrical, and plumbing, ensuring that repairs are made before problems escalate.
In Saudi Arabia, where extreme heat and other environmental factors can accelerate wear and tear on infrastructure, predictive maintenance helps to reduce costs and extend the life of critical assets. The ability to monitor infrastructure remotely and make adjustments in real-time significantly enhances operational efficiency.
Transport and Mobility Networks
Digital twins are poised to revolutionize urban transportation networks, and Saudi Arabia’s large-scale public transport projects are a prime example. The Riyadh Metro, for instance, will benefit from digital twin technology in its planning and operations. A digital twin of the metro system can simulate traffic, predict crowd patterns, and monitor train performance, ensuring efficient and smooth operations once the system is up and running.
Furthermore, digital twins can be used to optimize the integration of autonomous vehicles, electric transportation, and other smart mobility solutions within urban areas. For instance, traffic patterns and public transportation systems can be analyzed in real-time, allowing for more efficient routing and better utilization of resources
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of digital twins are immense, there are challenges to consider. The implementation of this technology requires substantial investment in data infrastructure, sensor networks, and software platforms. In addition, maintaining data security is crucial, as digital twins rely on vast amounts of data from connected devices and sensors. Ensuring that this data is protected against cyber threats is a top priority for cities implementing digital twins.
Moreover, the integration of digital twins across various sectors—energy, transport, construction, and more—requires collaboration among multiple stakeholders. The development of standardized protocols and frameworks will be key to ensuring that digital twins work seamlessly across different platforms and industries.
Conclusion: A New Era of Digital Infrastructure
As Saudi Arabia continues its transformation into a global hub of innovation, digital twin technology is playing a central role in shaping the future of urban development. From NEOM and Riyadh to smaller cities and rural areas, the potential for digital twins to optimize city planning, infrastructure management, and sustainability is vast.
For HYKAL and other architecture and engineering consultancies, digital twins offer exciting opportunities to design more efficient, sustainable, and resilient buildings and infrastructure. The integration of real-time data, advanced simulations, and predictive analytics will continue to redefine how cities are built and managed in Saudi Arabia and beyond. In the coming years, digital twins will not only improve the quality of life for residents but also pave the way for smarter, more connected urban environments that are capable of adapting to the challenges of the future.



